ASCP Collection Methods
Oracle ASCP Collection Methods:
There are three ways data can be collected into Oracle ASCP or APS or Value Chain Planning suite.
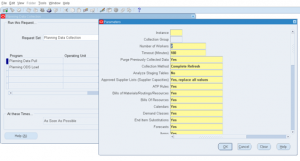
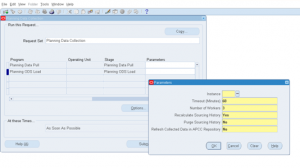
1) Standard Collections:
- Complete Refresh: In this all existing collected data will be purged and new data is imported.
- Targeted Refresh: Similar to Complete Refresh but for each object. You can selectively choose which objects require completed refresh, only those targeted objects will be refreshed.
- Net Change refresh: Imports only the changes that happened since last refresh. This methods work for supply / demand changes.
Objects supported under Net change mode.
- Sales Orders
- Reservations
- Master Production Schedules demands
- Master Demand Schedules demands
- WIP Component Demands
- WIP repetitive item demands
- Forecast demands
- User demands
- Master production schedule supplies
- User supplies
- Purchase Order Supplies
- On-hand supplies
- Work orders in Oracle WIP
- Resource availability
- Supplier capacity
- Bill of Material
- Routing Operations
- Components needed for Routing
- Resources attached to Routing
- Resource requirements for WIP Jobs
- Resources for WIP Jobs
- Items
- Item categories
- Capacity
Not supported objects for Net change Method
- Category sets
- Default item category
- Simulation sets
- Department resources
- Resource shift setup
- Hard reservations
- Projects or project tasks
- UOM
- Sourcing rules
- Bills of Resources
- Calendars
- Shipping networks
- Parameters
- Planners
- Suppliers
- Resource groups
- Demand classes
- Available To Promise rules
- Trading Partners
2) Continuous Collections:
Continuous collections systematically decides whether to run targeted refresh or net change based on a given threshold value (parameter). It runs based on snapshot data.
3) Legacy Collections:
This method is useful to import data from non-oracle ERP systems. Data is imported from flat files or from staging tables. Oracle provides the templates for each data/transaction objects, if data uploaded in that format, oracle imports data into planning server.