4.0 Workday Calendar Setup
Workday calendar controls the scheduling of Work Orders (WIP Job). You can define the working days ON/OFF, Shifts etc. Calendar setup is global but you can attach separate calendar for each Inventory organization.
Once you complete setting up the calendar you must build it.
Navigate to BOM responsibility -> Setup -> Calendars.
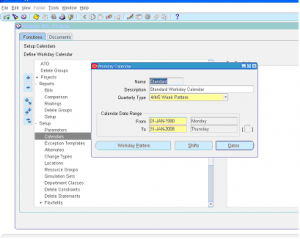
1 ) Enter the name of calendar
2 ) Enter the description of calendar
3 ) Enter calendar range i.e. start date and end date
4 ) Click on ‘Workday Pattern’ to se the workday pattern.
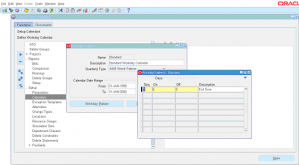
5 ) Enter the sequence to be followed, how many days off and how many days off. If your organization works from Monday to Friday and Saturday and Sunday are holidays, then choose calendar start date as Monday then set ‘5’ days ON and ‘2’ days OFF.
Enter the description of sequence and close the window.
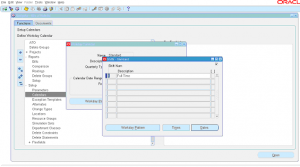
6 ) Click on ‘Shifts’ to enter working shift information
7 ) Enter the shift number and description, click on ‘times’ to enter shift start and end times.
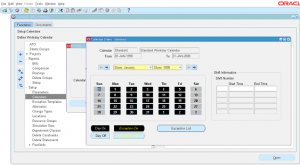
8 ) Click on Dates
9 ) Click on any date to make it exception i.e. work day OFF if it ON and viceversa.
10 ) Alternately you can click on ‘Exception List’ to manually enter exception date or import existing exception template. Exception template holds the holidays etc that can be applied to a calendar.
11) Once you finish Save the calendar and Build the calendar (Tools -> Build).